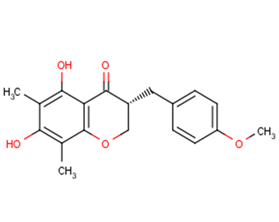
Methylophiopogonanone B
CAS No. 74805-91-7
Methylophiopogonanone B( —— )
Catalog No. M19070 CAS No. 74805-91-7
Methylophiopogonanone B (MOPB) induces cell morphological change and Rho activation via melanocyte dendrite retraction and stress fiber formation.
Purity : >98% (HPLC)
 COA
COA
 Datasheet
Datasheet
 HNMR
HNMR
 HPLC
HPLC
 MSDS
MSDS
 Handing Instructions
Handing Instructions
| Size | Price / USD | Stock | Quantity |
| 5MG | 426 | In Stock |


|
| 10MG | 626 | In Stock |


|
| 25MG | 981 | In Stock |


|
| 50MG | 1323 | In Stock |


|
| 100MG | Get Quote | In Stock |


|
| 200MG | Get Quote | In Stock |


|
| 500MG | Get Quote | In Stock |


|
| 1G | Get Quote | In Stock |


|
Biological Information
-
Product NameMethylophiopogonanone B
-
NoteResearch use only, not for human use.
-
Brief DescriptionMethylophiopogonanone B (MOPB) induces cell morphological change and Rho activation via melanocyte dendrite retraction and stress fiber formation.
-
DescriptionMethylophiopogonanone B (MOPB) induces cell morphological change and Rho activation via melanocyte dendrite retraction and stress fiber formation.
-
In Vitro——
-
In Vivo——
-
Synonyms——
-
PathwayOthers
-
TargetOther Targets
-
RecptorOthers
-
Research AreaOthers-Field
-
Indication——
Chemical Information
-
CAS Number74805-91-7
-
Formula Weight328.36
-
Molecular FormulaC19H20O5
-
Purity>98% (HPLC)
-
SolubilityIn Vitro:?DMSO : 100 mg/mL (304.54 mM)
-
SMILESCC1=C(C2=C(C(=C1O)C)OCC(C2=O)CC3=CC=C(C=C3)OC)O
-
Chemical Name——
Shipping & Storage Information
-
Storage(-20℃)
-
ShippingWith Ice Pack
-
Stability≥ 2 years
Reference
molnova catalog



related products
-
Picumast
Picumast shows antiallergic activity and can be utilized in the treatment of asthma. Picumast may be used in the treatment of therapeutic allergic airway diseases.
-
Stepharine
Alkaloids.
-
BAM - 18P
BAM - 18P



 Cart
Cart
 sales@molnova.com
sales@molnova.com


